The hum of servers, the flicker of screens, the seamless connection across continents – these aren't just background elements of our lives; they are the very fabric woven by Technological & Digital Resources. From the moment you check your phone for the weather to the complex algorithms predicting market trends, these innovations are the unseen architects shaping our productivity, powering our economies, and enriching our daily experiences. They're more than just tools; they're enablers, constantly evolving, and utterly indispensable in the modern world.
At a Glance: Understanding Technological & Digital Resources
- What they are: Elements born from scientific-technical innovation that make tasks easier, faster, or possible. Digital resources are their electronic, network-enabled subset.
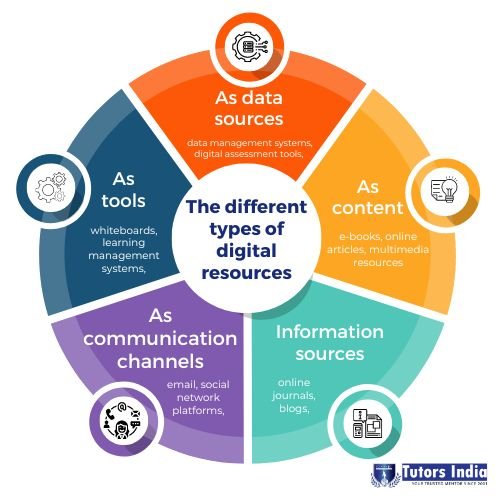
- Key Types: Physical hardware (computers, smartphones), intangible software (operating systems, apps), online platforms (social media, e-learning), and digital information (e-books, online articles).
- Defining Traits: Electronic nature, reliance on data, interconnectedness, scalability, dynamism, interactivity, and constant evolution.
- Why they're crucial: Boost productivity, enhance communication, provide vast information access, drive innovation, offer convenience, and reduce costs.
- How to use them wisely: Stay updated, prioritize cybersecurity, develop skills, embrace innovation, ensure accessibility, and critically evaluate information.
Beyond the Buzzwords: What Are Technological & Digital Resources?
Let's strip away the jargon and get to the core. At its heart, a technological resource is anything, tangible or intangible, that emerges from scientific innovation to make our work and lives better. Think of it as a force multiplier: it enables you to do more, faster, and often, with greater accuracy, than you ever could without it.
Digital resources are a specific, powerful subset of this. They encompass everything from the device you're reading this on to the vast ocean of data, software, and online services that make modern life tick. Whether it's an app on your phone, a website, a cloud storage service, or even the underlying network infrastructure, if it's accessed and processed electronically, it's a digital resource. It’s the engine that powers our always-on, interconnected world.
The Pillars of Modern Life: Why These Resources Matter
Imagine a day without digital tools. No email, no instant messaging, no online maps, no remote work, no streaming entertainment. It's a stark reminder of just how deeply these resources are integrated into every aspect of our existence. Their importance isn't just about convenience; it's fundamental to societal progress and individual empowerment.
- Unleashing Productivity and Efficiency: From project management software that streamlines workflows to automation tools that handle repetitive tasks, these resources are designed to maximize output. They reduce manual effort, minimize errors, and free up human intelligence for more creative and strategic endeavors.
- Bridging Distances: Communication and Collaboration: The internet and related digital tools have shrunk the globe. Video conferencing, collaborative document editing, and instant messaging platforms mean teams can work together across time zones and geographies, making global projects and remote work not just possible, but highly effective.
- A Universe of Knowledge: Access to Information: Need to learn a new skill? Research a complex topic? Find the latest news? Digital resources like online databases, e-learning platforms, academic journals, and search engines put virtually all human knowledge at your fingertips. This democratized access to information fuels continuous learning and informed decision-making.
- Sparking Innovation and Entrepreneurship: The barrier to entry for new ideas has plummeted thanks to digital resources. Cloud computing, open-source software, and digital marketing tools allow startups to launch with minimal overhead, experiment rapidly, and reach global audiences. Entire industries, from ride-sharing to online retail, owe their existence to these technological leaps.
- Convenience and Accessibility for All: Digital resources often break down geographical and physical barriers. Online services are available 24/7, from anywhere with an internet connection. Furthermore, with thoughtful design, they can offer enhanced accessibility features, empowering individuals with disabilities to participate more fully in the digital world. This is a significant advantage, ensuring broader participation, whether it's for education, employment, or connecting with peers, much like specialized programs can offer unique advantages for specific communities, for example, students looking for Marvel Rivals college perks.
- Cost-Effectiveness and Sustainability: Digital solutions reduce the need for physical storage, printing, and distribution. Think of e-books replacing physical libraries, or cloud storage supplanting rows of filing cabinets. This not only saves money but also minimizes environmental impact.
- Always Current, Always Relevant: Unlike printed materials, digital information can be updated and revised instantly. This dynamic nature ensures that data, educational content, and product information remain accurate and current, providing users with the most reliable insights available.
Navigating the Digital Landscape: A Taxonomy of Resources
The world of technological and digital resources is vast and varied. Understanding the different categories helps you leverage them more effectively.
Tangible vs. Intangible: The Foundation
First, let's distinguish between the physical and the abstract:
- Tangible Technological Resources: These are the physical objects you can touch and feel. They are the machinery and concrete elements that enable digital operations.
- Examples: Computers, laptops, smartphones, tablets, servers, routers, printers, scanners, smart home devices, specialized robotics hardware.
- Intangible Technological Resources: These are the incorporeal, abstract elements—the brains and networks that make the tangible resources useful.
- Examples: Software (operating systems, apps), the Internet itself, productivity suites, database management systems, AI/ML libraries, web development frameworks.
Specific Types of Digital Resources
Building on the tangible/intangible divide, here's a closer look at the key types you interact with daily:
- Connectivity Essentials: These are the invisible highways and byways that allow digital resources to communicate. Without them, our digital world grinds to a halt.
- Examples: The Internet, broadband connections, Wi-Fi, Ethernet, mobile data (5G, LTE), VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), telecommunications infrastructure.
- Hardware: The Physical Backbone: These are the devices that host and execute digital processes.
- Examples:
- Personal Devices: Laptops, desktops, smartphones, tablets.
- Network Infrastructure: Routers, switches, modems, firewalls.
- Peripherals: Printers, scanners, webcams, external storage.
- Enterprise Hardware: Servers, data centers.
- Software: The Operating Minds: Software provides instructions and functionality, making hardware useful.
- Examples:
- Operating Systems (OS): Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS.
- Productivity Suites: Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, PowerPoint), Google Workspace (Docs, Sheets, Slides), LibreOffice.
- Specialized Software: CAD software for engineers, video editing suites for creatives (Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve), medical imaging software, financial modeling tools.
- Development Tools: Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), web frameworks (React, Angular), AI/ML libraries (TensorFlow, PyTorch).
- Digital Platforms: Online Ecosystems: These are online services that host various functionalities and connect users for specific purposes.
- Examples:
- Professional Networking: LinkedIn.
- Project Management: Trello, Asana, Jira.
- E-learning: Coursera, Udemy, edX, Khan Academy.
- Blogging/Content Creation: Medium, WordPress.
- Social Media: Facebook, Instagram, Twitter/X, TikTok.
- E-commerce: Amazon, Shopify.
- Cloud Computing: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud (offering Infrastructure as a Service - IaaS, Platform as a Service - PaaS, Software as a Service - SaaS).
- Digital Information Resources: Knowledge at Your Fingertips: These are sources of information stored and accessed electronically.
- Examples: E-books, online articles, academic journals, research databases (Google Scholar, ScienceDirect), online encyclopedias (Wikipedia), government publications, digital archives.
- Advanced Technologies: The Cutting Edge: These represent the forefront of innovation, often integrating multiple resource types.
- Examples:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML): Tools for data analysis, natural language processing, predictive modeling.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Smart home devices, wearable tech, industrial sensors.
- Virtual Reality (VR) / Augmented Reality (AR): Immersive experiences and overlaid digital information.
- Blockchain & Cryptocurrency: Distributed ledger technologies for secure transactions and data management.
- Cybersecurity Tools: Antivirus software, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption.
Unpacking the DNA: Key Characteristics of Digital Resources
What makes digital resources so powerful and distinct? Several core characteristics define them:
- Electronic Nature: The most fundamental trait. All digital resources are accessed, stored, and processed using electronic signals and systems. They live in the digital realm.
- Data-Driven: Their functionality heavily relies on data—collecting it, processing it, analyzing it, and presenting it. Data is the fuel that powers almost every digital resource.
- Interconnectedness & Networkability: Digital resources are designed to connect. Through networks like the internet, they can be shared, accessed, and interact with each other globally, creating complex ecosystems.
- Scalability & Flexibility: One of their greatest strengths. Digital resources can often be replicated, distributed, updated, modified, and adapted with relative ease and at low cost, allowing for rapid expansion or changes.
- Dynamic Nature: Unlike static physical artifacts, digital content can be easily updated, revised, and personalized. This ensures information remains current and relevant.
- Interactivity: Users aren't just passive consumers; they can engage with digital resources through inputs, feedback, and customization, leading to more personalized and effective experiences.
- Constant Evolution & Innovation: The digital landscape is in perpetual motion. New technologies, platforms, and features emerge constantly, driving continuous improvement and opening up new possibilities.
Harnessing the Power: Best Practices for Leveraging & Creating Digital Resources
Simply having access to these resources isn't enough; knowing how to effectively leverage them—and even create your own—is where real advantage lies.
- Stay Current with Advancements: The tech world moves fast. Regularly research new tools, software updates, and emerging technologies relevant to your field or interests. Subscribing to tech news, attending webinars, and following industry leaders can keep you informed.
- Invest in Robust Cybersecurity: With great power comes great responsibility, and digital resources bring cyber risks. Implement strong passwords, use multi-factor authentication, keep software updated, and invest in reliable antivirus and firewall solutions. For organizations, regular security audits and employee training are non-negotiable.
- Develop Key Digital Skills: Don't just consume technology; understand how to use it proficiently. Invest time in learning new software, data analysis techniques, or even basic coding. Platforms like Coursera and Udemy offer extensive courses.
- Foster a Culture of Innovation and Experimentation: Encourage curiosity and a willingness to try new tools and methods. Create a safe space for testing new digital resources without fear of failure. Sometimes, the most unexpected tools yield the biggest breakthroughs.
- Emphasize Data-Driven Decision-Making: Leverage the analytical capabilities of digital resources. Collect relevant data, analyze it for insights, and use these insights to inform your strategies and decisions, rather than relying on guesswork.
- Ensure Accessibility and Usability: When creating or selecting digital resources, prioritize user experience. They should be intuitive, easy to navigate, and accessible to the widest possible audience, including those with disabilities.
- Provide Clear, Concise Information with High-Quality Multimedia: If you're creating digital information (e.g., a website, an e-book), present it clearly. Use high-quality visuals, videos, and interactive elements to enhance engagement and comprehension. Avoid jargon where simpler language suffices.
- Maintain Accuracy and Currency: Regularly update and revise your digital content. Outdated or incorrect information quickly loses credibility. Establish a review schedule to ensure your resources remain accurate and relevant.
- Critically Evaluate Digital Information Sources: Not all information online is reliable. Teach yourself (and others) to assess the credibility of sources by checking authors, publication dates, evidence, and potential biases. Look for established, reputable sources.
Common Questions & Misconceptions
"Aren't 'technological resources' just computers and software?"
While computers and software are prime examples, the definition is broader. A complex specialized machine in a factory is a technological resource, even if it's primarily mechanical, as long as it's derived from scientific-technical innovation to facilitate work. Digital resources are specifically the electronic and networked subset of these.
"How do I choose the 'right' digital resource for my needs?"
Start by defining your problem or goal. What do you need to achieve? Then, research tools that address that specific need. Consider:
- Functionality: Does it do what you need it to do?
- Ease of Use: Is the learning curve manageable?
- Cost: Does it fit your budget (including subscription fees)?
- Integration: Does it work well with your existing tools?
- Security: Are your data and privacy protected?
- Support: Is there good customer service or community support?
- Scalability: Can it grow with your needs?
"Is relying too much on digital resources a bad thing?"
Like any powerful tool, over-reliance without critical thought can have downsides, such as digital fatigue, privacy concerns, and the potential for skill atrophy in non-digital areas. The key is balance: leveraging the efficiency and power of digital tools while maintaining critical thinking, personal connection, and a healthy relationship with technology.
Your Next Steps: Building a Future with Technology
The journey into the world of technological and digital resources isn't a destination; it's a continuous expedition. These tools are no longer optional accessories but fundamental drivers of success, innovation, and connection in every sphere of life.
Your immediate action items should be clear:
- Audit Your Current Toolkit: Take stock of the digital resources you currently use, both personally and professionally. Are they serving you effectively? Are there gaps?
- Identify Growth Areas: Pinpoint one or two areas where better use of digital resources could significantly improve your productivity, learning, or impact.
- Commit to Continuous Learning: Choose one new digital skill or platform to explore this month. It could be learning advanced spreadsheet functions, trying a new project management app, or delving into the basics of data visualization.
- Prioritize Digital Wellness: While embracing technology, remember to set boundaries. Schedule screen-free time, be mindful of your digital consumption, and protect your online privacy.
By proactively engaging with, understanding, and ethically leveraging technological and digital resources, you're not just keeping up with the modern world; you're actively shaping your future within it. The power is truly at your fingertips.